
Thin film interference is the phenomenon that occurs when light reflects off the top and bottom surfaces of a thin film of material, such as a layer of oil on water. Here are some key points to remember about thin film interference: The λ in the material, however, is different from λ in the airĪlso occurs if the thickness is λ, 1.5λ, 2λ, 2.5λ…Īlso occurs if the thickness is 0.75λ, 1.25λ, 1,75λ, 2.25λ… The index of refraction of the first substance * the wavelength of light through that first substance = The index of refraction of the second substance * the wavelength of light through the second substance. Now, how do we calculate the wavelength inside the material? We start off with this equation, which hopefully looks familiar: The total distance that the wave travels is twice the thickness of the material.įor destructive interference- the total distance traveled must be a multiple of a whole wavelength.įor constructive interference- the total distance traveled must be an odd multiple of half a wavelength. Keep in mind that the wave that’s reflected from the front undergoes a 180^o 180 ophase change, but the wave reflected from the back doesn’t. Some interfere destructively their wavelengths are absent from the reflection. Some of the reflected waves interfere constructively, making those wavelengths more intense. In the figure above, when light hits the thin material, some of it is reflected from the first surface (front) and some from the secondary surface (back).

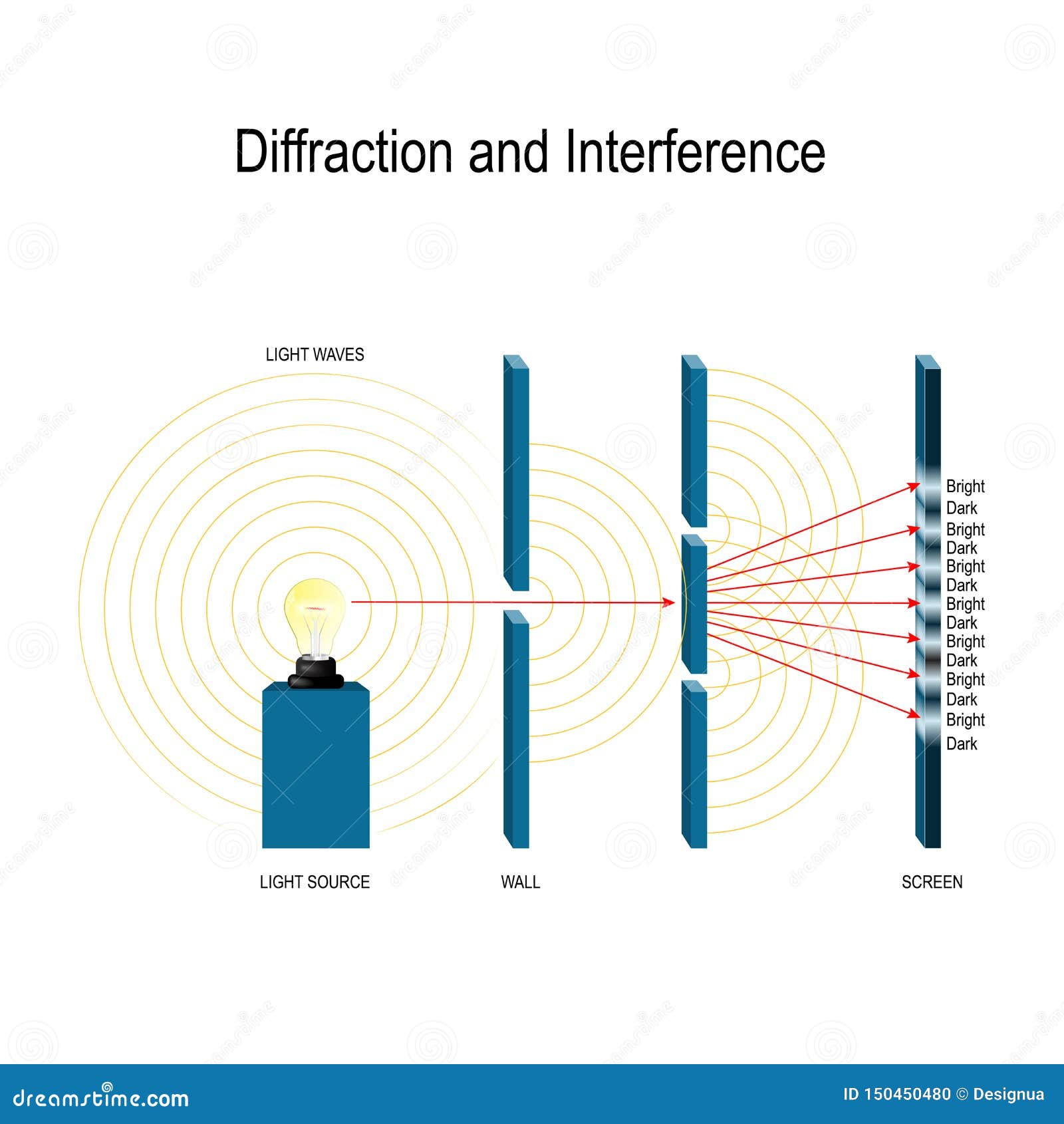
This is easily observable when a wave from a coherent(which means that the phase difference of the wave remains constant) source passes through a slit that’s similar in size to its wavelength. Let’s expand a bit more on diffraction: what is it? You can think of diffraction as the spreading of waves when they meet an obstacle/slit. The intensity of constructive interference is maximized when the amplitudes of the interfering waves are equal, and the intensity of destructive interference is maximized when the amplitudes of the interfering waves are equal and opposite. The intensity of interference is determined by the relative amplitudes and phases of the interfering waves. This occurs when the waves are out of phase, or when the difference in their phase is an odd integer multiple of π.Ĭonstructive and destructive interference can be observed in a variety of situations, including sound waves, light waves, and water waves. This occurs when the waves are in phase, or when the difference in their phase is an integer multiple of 2π.ĭestructive interference occurs when the amplitudes of two or more waves combine to produce a wave with a smaller amplitude. Interference can either enhance or cancel out the amplitude of the waves, depending on the phase relationship between the waves.Ĭonstructive interference occurs when the amplitudes of two or more waves combine to produce a wave with a greater amplitude. Interference is the phenomenon that occurs when two or more waves overlap. Here are some key points about constructive and destructive interference: Destructive Interference Taken from Wikimedia Commons


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
